# 문제점
이전 프로젝트에선 세션/쿠키 인증 방식으로 로그인 기능을 구현했고, 이를 위한 로직을 직접 코드로 작성했었습니다. 그로 인해 제가 직접 구현된 로직 내에서 발생할 수 있는 에러의 위험은 높았고, 보안성에 대한 완성도도 높지 못해 핵심 정보에 대한 노출 위험도 높았다고 볼 수 있습니다.
이를 발전시키기 위해 Spring에서 오직 인증, 인가 처리를 위해서만 제공하는 Spring Security를 가져와 활용해보기로 했습니다.
# 해결방안
Spring Security란?
Spring Security는 Spring 기반 애플리케이션의 보안을 담당하는 스프링 하위 Framework로써 ‘인증(Authentication)’과 ‘인가(Authorization)’에 대한 부분을 Filter의 흐름에 따라 처리합니다.
또한 Spring Security 많은 보안 관련 옵션들을 제공해주어 개발자가 보안 로직을 하나씩 작성하지 않아도 되는 편리성을 제공하고,인증, 인가 처리 로직에 대한 독립적인 운용이 가능하도록 기능을 제공해줍니다.
Spring Security 동작 원리
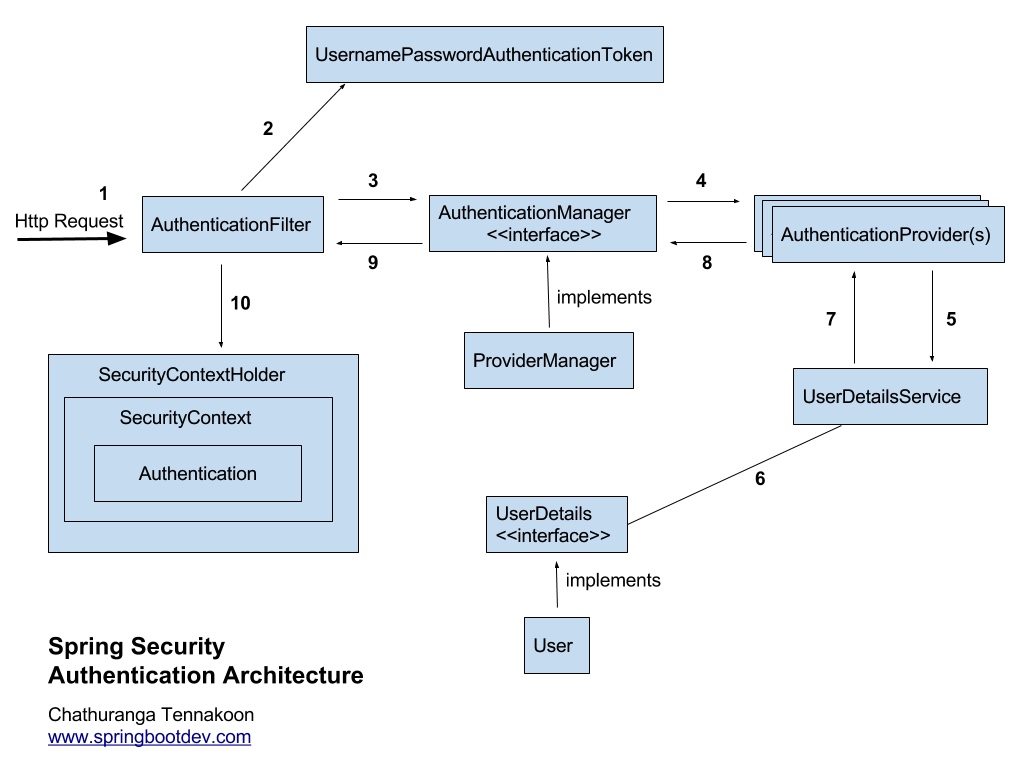
Spring Security의 동작 원리는 다음과 같습니다.
요청 수신 사용자가 form을 통해 로그인 정보가 담긴 Request를 보낸다.
토큰 생성 AuthenticationFilter가 요청을 받아서 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken토큰(인증용 객체)을 생성 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken은 해당 요청을 처리할 수 있는 Provider을 찾는데 사용
AuthenticationFilter로 부터 인증용 객체를 전달 받는다. Authentication Manager에게 처리 위임을 한다. 그리고 위임 받은Authentication Manager는 List형태로 Provider들을 갖고 있다.
Token을 처리할 수 있는 Authentication Provider 선택 실제 인증을 할 AuthenticationProvider에게 인증용 객체를 다시 전달한다.
인증 절차 인증 절차가 시작되면 AuthenticationProvider 인터페이스가 실행되고 DB에 있는 사용자의 정보와 화면에서 입력한 로그인 정보를 비교한다.
UserDetailsService의 loadUserByUsername메소드 수행 AuthenticationProvider 인터페이스에서는 authenticate() 메소드를 오버라이딩 하게 되는데 이 메소드의 파라미터인 인증용 객체로 화면에서 입력한 로그인 정보를 가져올 수 있다.
AuthenticationProvider 인터페이스에서 DB에 있는 사용자의 정보를 가져오려면, UserDetailsService 인터페이스를 사용한다.
UserDetailsService 인터페이스는 화면에서 입력한 사용자의 username으로 loadUserByUsername() 메소드를 호출하여 DB에 있는 사용자의 정보를 UserDetails 타입으로 가져온다. 만약 사용자가 존재하지 않으면 예외를 던진다. 이렇게 DB에서 가져온 이용자의 정보와 화면에서 입력한 로그인 정보를 비교하게 되고, 일치하면 Authentication 참조를 리턴하고, 일치 하지 않으면 예외를 던진다.
인증이 완료되면 사용자 정보를 가진 Authentication 객체를 SecurityContextHolder에 담은 이후 AuthenticationSuccessHandle를 실행한다.(실패시 AuthenticationFailureHandler를 실행한다.)
클래스별 역할
AuthenticationFilter
- 사용자로부터 전달된 Request 객체를 가지고 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken 객체를 생성한다.
- 생성된 객체를 AuthenticationManager에 넘긴다.
- 인증된 Authentication 객체를 전달받아 SecurityContextHolder에 저장한다.
AuthenticationManager
- 여러개의 AuthenticationProvider 구현체를 가지고 요청에 맞는 구현체에 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken을 전달한다.
AuthenticationProvider
- 실질적으로 인증 절차가 이뤄지는 곳이다.
- UserDetailsService로부터 DB에 저장된 사용자 정보와 비교 후 넘어온 리턴 객체를 가지고 Authentication 객체를 생성하거나 인증되지 못하는 경우 예외를 넘겨주는 역할을 한다.
UserDetailsService
- DB에 접근해 넘어온 사용자 정보와 일치하는 정보를 조회한다.
- 조회에 성공하면 UserDetails 타입의 객체를 리턴한다.
SecurityContextHolder
- 프로젝트 내 어디에서든 인증이 완료된 사용자 정보를 호출할 수 있도록 해주는 클래스이다.
프로젝트 내 구현 코드
JwtFilter
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
/**
* Request Header 에서 가져온 토큰을 필터링하는 과정을 담당
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class JwtFilter implements Filter {
private final TokenProvider tokenProvider;
/**
* 실제 필터링 로직은 doFilter 내부에 작성 jwt 토큰의 인증 정보를 SecurityContext에 저장하는 역할.
*/
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request,ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
// Request 객체에서 담겨져 온 토큰을 조회
HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest = (HttpServletRequest) request;
String jwt = resolveToken(httpServletRequest);
String requestURI = httpServletRequest.getRequestURI();
if (StringUtils.hasText(jwt) && tokenProvider.validateToken(jwt)) {
// Provider에 의해 인증 절차를 진행. 인증이 완료되면 Authentication 객체를 리턴
Authentication authentication = tokenProvider.getAuthentication(jwt);
// Authentication 객체를 SecurityContextHolder에 저장
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authentication);
log.debug("Security Context에 '{}' 인증 정보 저장, uri: {}", authentication.getName(), requestURI);
} else {
log.debug("유효한 JWT 토큰이 없습니다, uri: {}", requestURI);
}
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
/**
* request header에서 토큰 정보를 꺼내오는 메소드.
*/
private String resolveToken(HttpServletRequest request) {
String bearerToken = request.getHeader(AUTHORIZATION_HEADER);
if (StringUtils.hasText(bearerToken) && bearerToken.startsWith("Bearer ")) {
return bearerToken.substring(7);
}
return null;
}
}
TokenProvider
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
/**
* TokenProvider 클래스.
* 토큰 생성 및 유효성 검사, Authentication 객체 생성을 담당
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class TokenProvider implements InitializingBean {
private final String secret;
private final long tokenValidityInMilliseconds;
private Key key;
public TokenProvider(
@Value("${jwt.secret}") String secret,
@Value("${jwt.token-validity-in-seconds}") long tokenValidityInSeconds) {
this.secret = secret;
this.tokenValidityInMilliseconds = tokenValidityInSeconds * 1000;
}
/**
* 빈이 생성이 되고 의존성 주입이 되고 난 후에 주입받은 secret 값을 Base64 Decode 해서 key 변수에 할당.
*/
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
byte[] keyBytes = Decoders.BASE64.decode(secret);
this.key = Keys.hmacShaKeyFor(keyBytes);
}
/**
* Authentication 객체의 권한정보를 이용해서 토큰을 생성하는 createToken 메소드 추가.
*/
public String createToken(Authentication authentication, String userName) {
String authorities = authentication.getAuthorities()
.stream()
.map(GrantedAuthority::getAuthority)
.collect(Collectors.joining(","));
long now = (new Date()).getTime();
Date validity = new Date(now + this.tokenValidityInMilliseconds);
Claims claims = Jwts.claims()
.setSubject(authentication.getName())
.setExpiration(validity);
claims.put(AUTHORITIES_KEY, authorities);
claims.put(NAME_KEY, userName);
return Jwts.builder()
.setClaims(claims)
.signWith(key, SignatureAlgorithm.HS512)
.compact();
}
/**
* token에 담겨있는 정보를 이용해 Authentication 객체를 리턴하는 메소드 생성.
*/
public Authentication getAuthentication(String token) {
Claims claims = Jwts.parserBuilder()
.setSigningKey(key)
.build()
.parseClaimsJws(token)
.getBody();
List<SimpleGrantedAuthority> authorities = Arrays
.stream(claims.get(AUTHORITIES_KEY).toString().split(","))
.map(SimpleGrantedAuthority::new)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
User principal = new User(claims.getSubject(), "", authorities);
return new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(principal, "", authorities);
}
/**
* 토큰의 유효성 검증을 수행하는 validateToken 메소드 추가.
*/
public boolean validateToken(String token) {
try {
Jwts.parserBuilder().setSigningKey(key).build().parseClaimsJws(token);
return true;
} catch (io.jsonwebtoken.security.SecurityException | MalformedJwtException e) {
log.info("잘못된 JWT 서명입니다.");
} catch (ExpiredJwtException e) {
log.info("만료된 JWT 토큰입니다.");
} catch (UnsupportedJwtException e) {
log.info("지원되지 않는 JWT 토큰입니다.");
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
log.info("JWT 토큰이 잘못되었습니다.");
}
return false;
}
CustomUserDetailsSevice
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
@Slf4j
@Service
@Transactional(readOnly = true)
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class CustomUserDetailsService implements UserDetailsService {
private final UserRepository userRepository;
// DB 에 저장된 사용자 정보와 일치하는지 여부를 판단
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
User user = userRepository.findById(Integer.parseInt(username))
.orElseThrow(() -> new UsernameNotFoundException(username + " 존재하지 않는 username 입니다."));
return createUserDetails(user);
}
private UserDetails createUserDetails(User user) {
return new org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User(
String.valueOf(user.getId()),
user.getPassword(),
List.of(new SimpleGrantedAuthority(user.getRole().toString()))
);
}
}
위 구현 클래스 외에도 Spring Security를 사용하기 위한 Config 클래스도 필요로 합니다.
JwtSecurityConfig
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
/**
* JwtFilter를 SecurityConfig에 적용할 때 사용할 JwtSecurityConfig.
*/
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class JwtSecurityConfig extends
SecurityConfigurerAdapter<DefaultSecurityFilterChain, HttpSecurity> {
private final JwtFilter jwtFilter;
/**
* JwtFilter를 Security 로직에 필터를 등록.
*/
@Override
public void configure(HttpSecurity http) {
// Security 로직에 필터를 등록
http.addFilterBefore(jwtFilter, UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class);
}
}
SecurityConfig
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
/**
* Spring Security 관련 설정 파일.
*/
@EnableWebSecurity
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true)
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
private final JwtAuthenticationEntryPoint jwtAuthenticationEntryPoint;
private final JwtAccessDeniedHandler jwtAccessDeniedHandler;
private final JwtSecurityConfig jwtSecurityConfig;
/**
* 암호화 방식 선택.
*/
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
/**
* 어플리케이션 자체에 넘어오는 요청에 대한 인증, 인가 관련 설정에 대한 메소드.
* 이 위치에서 제외된 API들은 Spring Security의 검증 대상 자체에서 제외됩니다.
*/
@Override
public void configure(WebSecurity web) throws Exception {
web
.ignoring()
.antMatchers("/chat/health/check")
.antMatchers("/ws/send/message")
.antMatchers("/ws/connect");
}
/**
* API 접근에 대한 인증 처리 관련 설정.
* 선택적으로 Spring Security에 의한 인증, 인가 절차 대상 및 방법을 설정할 수 있습니다.
*/
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.csrf().disable()
.exceptionHandling()
.authenticationEntryPoint(jwtAuthenticationEntryPoint)
.accessDeniedHandler(jwtAccessDeniedHandler)
.and()
.sessionManagement()
.sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.STATELESS)
// 인가 절차를 생략할 API를 지정
.and()
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/user/signup", "/user/login").permitAll()
// 그 외 API는 인증 절차 수행
.anyRequest().authenticated()
// JwtSecurityConfig 클래스 적용
.and()
.apply(jwtSecurityConfig);
}
}
# 마치며
이처럼 Spring Security는 인증과 인가에 대한 다양한 기능을 제공해줌으로써 어플리케이션 구현에 있어 큰 편리함과 안정성을 보장해줍니다. 다만 동작 원리가 복잡해 이를 제대로 이해하고 있지 못한다면 올바르게 활용하기 어려울 수 있기 때문에 정확한 이해가 필요합니다.
# 참고 자료
- https://velog.io/@seongwon97/Spring-Security-Spring-Security%EB%9E%80
- https://velog.io/@kyungwoon/Spring-Security-%EB%8F%99%EC%9E%91-%EC%9B%90%EB%A6%AC
- https://hose.tistory.com/10